Dibenzochrysene enables tightly controlled docking and stabilizes photoexcited states in dual-pore covalent organic frameworks†
Abstract
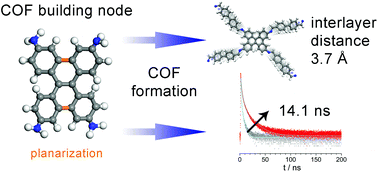
Covalent organic frameworks (COFs), consisting of covalently connected organic building units, combine attractive features such as crystallinity, open porosity and widely tunable physical properties. For optoelectronic applications, the incorporation of heteroatoms into a 2D COF has the potential to yield desired photophysical properties such as lower band gaps, but can also cause lateral offsets of adjacent layers. Here, we introduce dibenzo[g,p]chrysene (DBC) as a novel building block for the synthesis of highly crystalline and porous 2D dual-pore COFs showing interesting properties for optoelectronic applications. The newly synthesized terephthalaldehyde (TA), biphenyl (Biph), and thienothiophene (TT) DBC-COFs combine conjugation in the a,b-plane with a tight packing of adjacent layers guided through the molecular DBC node serving as specific docking site for successive layers. The resulting DBC-COFs exhibit a hexagonal dual-pore kagome geometry, which is comparable to COFs containing another molecular docking site, namely 4,4′,4′′,4′′′-(ethylene-1,1,2,2-tetrayl)-tetraaniline (ETTA). In this context, the respective interlayer distances decrease from about 4.6 Å in ETTA-COFs to about 3.6 Å in DBC-COFs, leading to well-defined hexagonally faceted single crystals sized about 50–100 nm. The TT DBC-COF features broad light absorption covering large parts of the visible spectrum, while Biph DBC-COF shows extraordinary excited state lifetimes exceeding 10 ns. In combination with the large number of recently developed linear conjugated building blocks, the new DBC tetra-connected node is expected to enable the synthesis of a large family of highly correlated and ordered 2D COFs with promising optoelectronic properties.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...