Prussian blue-coated lanthanide-doped core/shell/shell nanocrystals for NIR-II image-guided photothermal therapy†
Abstract
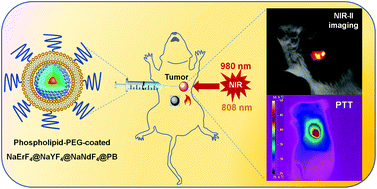
Lanthanide-doped nanoparticles have long been stereotyped for optical luminescence bioimaging. However, they are known to be unable to produce therapeutic abilities. Here, we describe a lanthanide-based theranostic agent, namely, prussian blue (PB)-coated NaErF4@NaYF4@NaNdF4 core/shell/shell nanocrystals encapsulated in a phospholipid PEG micelle (PEG-CSS@PB), which showed switched imaging and hyperthermia abilities under distinct near infrared (NIR) light activation. The erbium (Er3+)-enriched inner core nanocrystals (NaErF4) enabled the emission of tissue-penetrating luminescence (1525 nm) in the second biological window (NIR-II, 1000–1700 nm), which endowed high-resolution optical imaging of the blood vessels and tumors under ∼980 nm excitation. High neodymium (Nd3+) concentrations in the epitaxial outer NaNdF4 shell introduced maximum cross relaxation processes that converted the absorbed NIR light (∼808 nm) into heat at high efficiencies, thus providing abilities for photothermal therapy (PTT). Importantly, the coated Prussian blue (PB) increased light absorption by about 10-fold compared to the composite free of PB, thus entailing a high light-to-heat conversion efficiency of ∼50.5%. This commensurated with that of well-established gold nanorods. As a result, the PEG-CSS@PB nanoparticles with MTT-determined low toxicities resulted in ∼80% death of HeLa cells at a dose of 600 μg mL−1 under 808 nm laser irradiance (1 W cm−2) for 10 min. Moreover, utilizing the same light dose, a single PTT treatment in tumor-bearing BALB/c mice shrunk the tumor size by ∼12-fold compared to the tumors without treatment. Our results, here, constituted a solid step forward to entitle lanthanide-based nanoparticles as theranostic agents in nanomedicine studies.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...