Resolving single Cu nanoparticle oxidation and Kirkendall void formation with in situ plasmonic nanospectroscopy and electrodynamic simulations†
Abstract
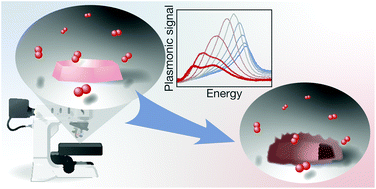
Copper nanostructures are ubiquitous in microelectronics and heterogeneous catalysis and their oxidation is a topic of high current interest and broad relevance. It relates to important questions, such as catalyst active phase, activity and selectivity, as well as fatal failure of microelectronic devices. Despite the obvious importance of understanding the mechanism of Cu nanostructure oxidation, numerous open questions remain, including under what conditions homogeneous oxide layer growth occurs and when the nanoscale Kirkendall void forms. Experimentally, this is not trivial to investigate because when a large number of nanoparticles are simultaneously probed, ensemble averaging makes rigorous conclusions difficult. On the other hand, when (in situ) electron-microscopy approaches with single nanoparticle resolution are applied, concerns about beam effects that may both reduce the oxide or prevent oxidation via the deposition and cross-linking of carbonaceous species cannot be neglected. In response we present how single particle plasmonic nanospectroscopy can be used for the in situ real time characterization of multiple individual Cu nanoparticles during oxidation. Our analysis of their optical response combined with post mortem electron microscopy imaging and detailed Finite-Difference Time-Domain electrodynamics simulations enables in situ identification of the oxidation mechanism both in the initial oxide shell growth phase and during Kirkendall void formation, as well as the transition between them. In a wider perspective, this work presents the foundation for the application of single particle plasmonic nanospectroscopy in investigations of the impact of parameters like particle size, shape and grain structure with respect to defects and grain boundaries on the oxidation of metal nanoparticles.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...