The effects of discrete and gradient mid-shell structures on the photoluminescence of single InP quantum dots†
Abstract
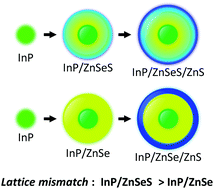
We investigated the dependence of the spectral diffusion and blinking behaviors of indium phosphide (InP) based core/shell/shell quantum dots (QDs) on their mid-shell compositions. We synthesized two types of core/shell/shell QDs having different mid-shell structures by controlling the shell thickness, the total sizes, and the selenium to sulfur ratios. The QDs with a discrete mid-shell (DS-QDs) exhibited a higher photoluminescence (PL) quantum yield (QY) and a narrower PL linewidth than the QDs with a gradient mid-shell (GS-QDs). By analyzing X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, and Raman spectra, we found that GS-QDs showed a larger lattice mismatch between the core and the shell than DS-QDs. Also, the spectral diffusion, PL blinking, Auger ionization efficiencies, and the lifetime blinking behavior on single QDs revealed that DS-QDs were nearly unaffected by the defect traps.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...