Raman and electrical transport properties of few-layered arsenic-doped black phosphorus†
Abstract
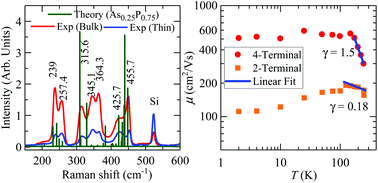
Black phosphorus (b-P) is an allotrope of phosphorus whose properties have attracted great attention. In contrast to other 2D compounds, or pristine b-P, the properties of b-P alloys have yet to be explored. In this report, we present a detailed study on the Raman spectra and on the temperature dependence of the electrical transport properties of As-doped black phosphorus (b-AsP) for an As fraction x = 0.25. The observed complex Raman spectra were interpreted with the support of Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations since each original mode splits in three due to P–P, P–As, and As–As bonds. Field-effect transistors (FET) fabricated from few-layered b-AsP exfoliated onto Si/SiO2 substrates exhibit hole-doped like conduction with a room temperature ON/OFF current ratio of ∼103 and an intrinsic field-effect mobility approaching ∼300 cm2 V−1 s−1 at 300 K which increases up to 600 cm2 V−1 s−1 at 100 K when measured via a 4-terminal method. Remarkably, these values are comparable to, or higher, than those initially reported for pristine b-P, indicating that this level of As doping is not detrimental to its transport properties. The ON to OFF current ratio is observed to increase up to 105 at 4 K. At high gate voltages b-AsP displays metallic behavior with the resistivity decreasing with decreasing temperature and saturating below T ∼100 K, indicating a gate-induced insulator to metal transition. Similarly to pristine b-P, its transport properties reveal a high anisotropy between armchair (AC) and zig-zag (ZZ) directions. Electronic band structure computed through periodic dispersion-corrected hybrid Density Functional Theory (DFT) indicate close proximity between the Fermi level and the top of the valence band(s) thus explaining its hole doped character. Our study shows that b-AsP has potential for optoelectronics applications that benefit from its anisotropic character and the ability to tune its band gap as a function of the number of layers and As content.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...