Enhanced broadband fluorescence detection of nucleic acids using multipolar gap-plasmons on biomimetic Au metasurfaces†
Abstract
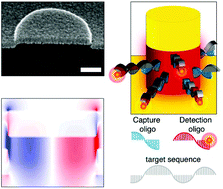
Recent studies on metal–insulator–metal-based plasmonic antennas have shown that emitters could couple with higher-order gap-plasmon modes in sub-10-nm gaps to overcome quenching. However, these gaps are often physically inaccessible for functionalization and are not scalably manufacturable. Here, using a simple biomimetic batch-fabrication, a plasmonic metasurface is created consisting of closely-coupled nanodisks and nanoholes in a metal–insulator–metal arrangement. The quadrupolar mode of this system exhibits strong broadband resonance in the visible-near-infrared regime with minimal absorptive losses and effectively supresses quenching, making it highly suitable for broadband plasmon-enhanced fluorescence. Functionalizing the accessible insulator nanogap, analytes are selectively immobilized onto the plasmonic hotspot enabling highly-localized detection. Sensing the streptavidin–biotin complex, a 91-, 288-, 403- and 501-fold fluorescence enhancement is observed for Alexa Fluor 555, 647, 750 and 790, respectively. Finally, the detection of single-stranded DNA (gag, CD4 and CCR5) analogues of genes studied in the pathogenesis of HIV-1 between 10 pM–10 μM concentrations and then CD4 mRNA in the lysate of transiently-transfected cells with a 5.4-fold increase in fluorescence intensity relative to an untransfected control is demonstrated. This outcome promises the use of biomimetic Au metasurfaces as platforms for robust detection of low-abundance nucleic acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...