CuS–MnS2 nano-flowers for magnetic resonance imaging guided photothermal/photodynamic therapy of ovarian cancer through necroptosis
Abstract
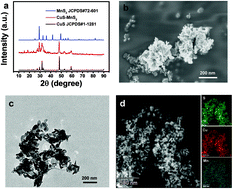
With a high incidence and high mortality rate, ovarian cancer presents a challenge for clinical practice. It is thus extremely urgent to investigate new diagnosis and therapy methods for the treatment of ovarian cancer. Ternary copper-based chalcogenide nanomaterials are attractive owing to their near infrared (NIR) response for cancer theranostic fields. However, improving the theranostic efficiency of these nanomaterials is challenging. Herein, CuS–MnS2 nano-flowers were easily synthesized and under NIR irradiation exhibited a relatively high photothermal conversion efficiency of 67.5% and a simultaneous reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation effect. Owing to these outstanding photothermal/photodynamic effects, excellent tumor ablation results could be achieved by the combined use of CuS–MnS2 nano-flowers and 808 nm NIR laser treatments. The main anticancer mechanism of CuS–MnS2 nano-flowers + NIR was likely necroptosis. In addition, the nano-flowers showed remarkable contrast enhancement according to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). These CuS–MnS2 nano-flowers could thus serve as a promising multifunctional nanotheranostic agent for MRI and as a photothermal/photodynamic cancer therapy agent through necroptosis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...