Enhancement of ultralow-intensity NIR light-triggered photodynamic therapy based on exo- and endogenous synergistic effects through combined glutathione-depletion chemotherapy†
Abstract
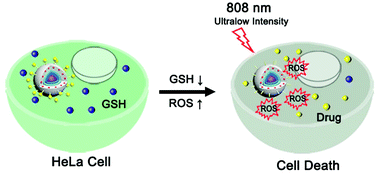
Although photodynamic therapy (PDT), which uses a photosensitizer (PS) to generate toxic reactive oxygen species (ROS) upon laser irradiation to kill cancer cells, has been widely applied, the relatively high laser intensity required causes photodamage to healthy neighboring cells and limits its success. Furthermore, glutathione (GSH, an antioxidant) is overexpressed in cancer cells, which can scavenge the generated ROS, thus lowering PDT efficacy. Herein, ultralow-intensity near-infrared (NIR) light-triggered PDT was developed and enhanced through combined GSH-depletion chemotherapy (Chemo) based on exo- and endogenous synergistic effects. Highly emissive upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs) were prepared and coated with a solid silica shell, which was used to encapsulate the PS rose bengal and bond the drug camptothecin with a disulfide-bond linker. The combination of highly emissive UCNPs and a matchable PS with an optimized loading dosage enabled ROS to be generated for PDT even upon 808 nm laser irradiation with ultralow intensity (0.30 W cm−2). According to the American National Standard, this laser intensity is below the maximum permissible exposure of skin (MPE, 0.33 W cm−2). Once the prepared nanoparticles endocytosed and encountered intracellular GSH, the disulfide-bond linker was cleaved by GSH, leading to drug release and GSH depletion. PDT was therefore simultaneously enhanced through the exogenous synergic effect of Chemo (namely, the “1 + 1 > 2” therapeutic effect) and the endogenous synergic effect as a result of GSH depletion. It was proven both in vitro and in vivo that this novel dual-synergistic Chemo/PDT system exhibits remarkable therapeutic efficacy with minimal photodamage to healthy neighboring cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...