Nanomechanical elasticity and fracture studies of lithium phosphate (LPO) and lithium tantalate (LTO) solid-state electrolytes†
Abstract
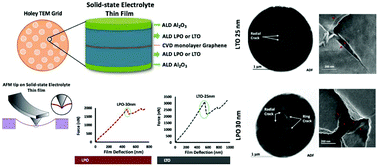
All-solid-state batteries (ASSBs) have attracted much attention due to their enhanced energy density and safety as compared to traditional liquid-based batteries. However, cyclic performance depreciates due to microcrack formation and propagation at the interface of the solid-state electrolytes (SSEs) and electrodes. Herein, we studied the elastic and fracture behavior of atomic layer deposition (ALD) synthesized glassy lithium phosphate (LPO) and lithium tantalate (LTO) thin films as promising candidates for SSEs. The mechanical behavior of ALD prepared SSE thin films with a thickness range of 5 nm to 30 nm over suspended single-layer graphene was studied using an atomic force microscope (AFM) film deflection technique. Scanning transmission electron microscopy (STEM) coupled with AFM was used for microstructural analysis. LTO films exhibited higher stiffness and higher fracture forces as compared to LPO films. Fracture in LTO films occurred directly under the indenter in a brittle fashion, while LPO films failed by a more complex fracture mechanism including significant plastic deformation prior to the onset of complete fracture. The results and methodology described in this work open a new window to identify the potential influence of SSEs mechanical performance on their operation in flexible ASSBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...