Single-particle enumeration-based ultrasensitive enzyme activity quantification with fluorescent polymer nanoparticles†
Abstract
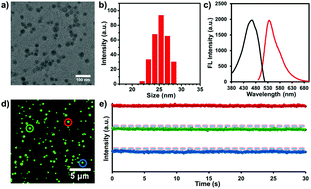
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) plays a vital role in nerve conduction through rapidly hydrolyzing the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) and is correlated with Alzheimer's disease. In this work, a label-free single-particle enumeration (SPE) method for the quantitative detection of acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activity is developed. The design is based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) between fluorescent conjugated polymer nanoparticles (FCPNPs) and MnO2 nanosheets. The fluorescence of FCPNPs can be effectively quenched by MnO2 nanosheets via hydrogen bonding interaction. In the presence of acetylcholinesterase (AChE), acetylthiocholine (ATCh) could be hydrolyzed to thiocholine (TCh), which can reduce MnO2 to Mn2+ and trigger the decomposition of MnO2 nanosheets. As a result, the fluorescence of FCPNPs is restored. Taking advantage of the superior brightness and stable fluorescence emission from individual FCPNPs, the accurate quantification of AChE is achieved by statistically counting the fluorescent particles on the glass slide surface. A linear range from 5 to 1600 μU mL−1 is obtained for AChE assay and the limit-of-detection (LOD) is 1.02 μU mL−1, which is far below the spectroscopic measurements in bulk solution. In the human serum sample, satisfactory recovery efficiencies are determined in a range of 91.0%–103.0%. Furthermore, pesticide carbaryl as an inhibitor of AChE activity was detected. The LOD is 1.12 pg mL−1 with linear responses ranging from 5 to 300 pg mL−1, which demonstrates the feasibility of this approach for AChE inhibitor screening. As a consequence, the label-free SPE-based method affords a promising platform for the sensitive detection of target molecules in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...