Stabilizing a high-voltage LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 cathode towards all solid state batteries: a Li–Al–Ti–P–O solid electrolyte nano-shell with a host material†
Abstract
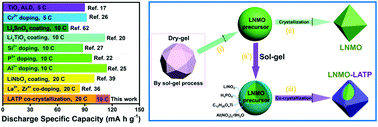
LiNi0.5Mn1.5O4 (LNMO) spinel has drawn increasing attention due to its high voltage, stabilized electrochemical performance and safety features as a cathode for lithium-ion batteries. However, the main challenge lies in its unstable surface structure, especially at elevated temperatures. In this paper, we decorate the LNMO precursor with a solid electrolyte of Li1.4Al0.4Ti1.6(PO4)3 (LATP) via a facile sol–gel method, followed by a co-crystallization process at 820 °C, to successfully generate a LATP modification shell at the surface of LNMO. The LATP modification shell could not only optimize the morphology of LNMO including the limitation of particle growth and control of crystalline orientation, but also realize ion doping during the co-crystallization process. By tuning the LATP contents, the 2 wt% LATP modification is found to be the most effective at balancing the interfacial stability and Li+ diffusion kinetics of LNMO, as well as enhancing its rate capability and capacity retention at high temperatures. As a result, the 2 wt% LATP-modified LNMO cathode exhibits a high reversible capacity of 84.8 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles with a capacity retention of 68.9%, and a superior rate capability (102.0 mA h g−1 at 20 C) at room temperature. Moreover, this electrode also delivers a good capacity retention of 85.7% after 100 cycles at 55 °C, which is ascribed to the stabilized interface with a LATP protective layer.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...