A dual-modal nanoprobe based on Eu(iii) complex–MnO2 nanosheet nanocomposites for time-gated luminescence–magnetic resonance imaging of glutathione in vitro and in vivo†
Abstract
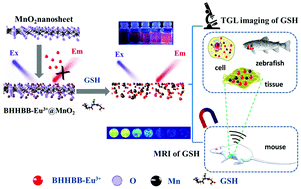
Dual-modal fluorescence–magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques have gained great interest in biomedical research and clinical practice, since they integrate the advantages of both imaging techniques and provide a useful approach to simultaneously investigate both molecular and anatomical information at the same biological structures. Herein, we report the construction of a dual-modal time-gated luminescence (TGL)/MRI nanoprobe, BHHBB–Eu3+@MnO2, for glutathione (GSH) by anchoring luminescent β-diketone-Eu3+ complexes on layered MnO2 nanosheets. The fabricated nanoprobe exhibited very week luminescence and MR signals since the luminescence of the Eu3+ complex was quenched by MnO2 nanosheets and Mn atoms were isolated from water. Upon exposure to GSH, the MnO2 nanosheets were rapidly and selectively reduced to Mn2+ ions, resulting in remarkable enhancements of TGL and MR signals simultaneously. The combination of TGL and MR detection modes enables the nanoprobe to be used for detecting GSH in a wide concentration range (1–1000 μM) and imaging GSH at different resolutions and depths ranging from the subcellular level to the whole body. Furthermore, the as-prepared nanoprobe exhibited a low cytotoxicity and good biocompatibility, rapid response rate, long-lived luminescence, and high sensitivity and selectivity for responding to GSH. These features allowed it to be successfully used for the TGL detection of GSH in human sera, TGL imaging of GSH in living cells and zebrafish, as well as dual-modal TGL/MR imaging of GSH in tumor-bearing mice. All of these results highlighted the applicability and advantages of the nanoprobe for detecting GSH in vitro and in vivo.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...