Optical response of magnetically actuated biocompatible membranes†
Abstract
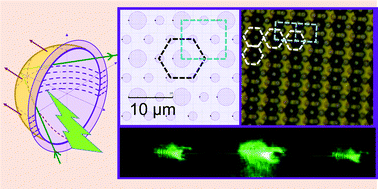
Biocompatible suspended magneto-elastic membranes were prepared. They consist of PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) films, with embedded arrays of micrometric magnetic pillars made with lithography techniques. For visible light wavelengths, our membranes constitute magnetically tunable optical diffraction gratings, in transmission and reflection. The optical response has been quantitatively correlated with membrane structure and deformation, through optical and magneto-mechanical models. In contrast to the case of planar membranes, the diffraction patterns measured in reflection and transmission vary very differently upon magnetic field application. Indeed, the reflected beam is largely affected by the membrane bending, whereas the transmitted beam remains almost unchanged. In reflection, even weak membrane deformation can produce significant changes of the diffraction patterns. This field-controlled optical response may be used in adaptive optical applications, photonic devices, and for biological applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...