Recyclable magnetic covalent organic framework for the extraction of marine biotoxins†
Abstract
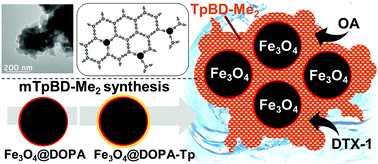
A novel procedure for the preparation of magnetic covalent organic frameworks (COFs) is reported. In situ functionalization of Fe3O4 with dopamine rapidly afforded amino-functionalized magnetic nanoparticles, which after decoration with a COF building block and subsequent COF growth gave access to magnetic composite mTpBD-Me2. The optimized synthesis conditions yielded crystalline and superparamagnetic material with no loss in surface area as compared to bulk COF. The composite material was employed for the first time in magnetic solid-phase extraction of marine biotoxins from seawater with high efficiency, where calculated maximum adsorption capacities of 812 mg g−1 and 830 mg g−1 were found for okadaic acid (OA) and dinophysistoxin-1 (DTX-1), respectively, corresponding to an increase of ∼500-fold for OA and ∼300-fold for DTX-1 as compared to the commonly used non-magnetic macroporous resins. Nearly quantitative desorption efficiency of both biotoxins was obtained using 2-propanol as solvent, rendering the composite materials recyclable with merely minor losses in adsorption capacity after five consecutive cycles of adsorption/desorption. In addition, retention of crystallinity after the adsorption cycles highlights the stability of the composite in seawater. These results illustrate the great efficiency of the novel material in biotoxin adsorption and show great promise for its application in environmental monitoring programs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...