Yolk–shell-structured microspheres composed of N-doped-carbon-coated NiMoO4 hollow nanospheres as superior performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
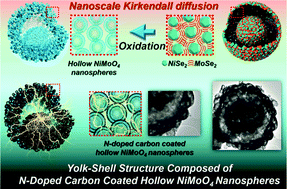
Novel yolk–shell-structured microspheres consisting of N-doped-carbon-coated metal–oxide hollow nanospheres are designed as efficient anode materials for lithium-ion batteries and synthesized via a spray pyrolysis process. A NiMoO4 yolk–shell architecture formed via spray pyrolysis is transformed into equally structured NiSe2–MoSe2 composite microspheres. Because of the complementary effect between the Ni and Mo components that prevents severe crystal growth during selenization, NiSe2–MoSe2 nanocrystals are uniformly distributed over the yolk–shell structure. Then, the yolk–shell-structured NiSe2–MoSe2 microspheres are oxidized, which yields microspheres composed of NiMoO4 hollow nanospheres by nanoscale Kirkendall diffusion. Uniform coating with polydopamine and a subsequent carbonization process produce uniquely structured microspheres consisting of N-doped-carbon-coated NiMoO4 hollow nanospheres. The discharge capacity of the yolk–shell-structured NiMoO4–C composite microspheres for the 500th cycle at a current density of 3.0 A g−1 is 862 mA h g−1. In addition, the NiMoO4–C composite microspheres show a high reversible capacity of 757 mA h g−1 even at an extremely high current density of 10 A g−1. The synergetic effect between the hollow nanospheres comprising the yolk–shell structure and the N-doped carbon coating layer results in the excellent lithium-ion storage performance of the NiMoO4–C composite microspheres.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...