Realization of an efficient electron source by ultraviolet-light-assisted field emission from a one-dimensional ZnO nanorods/n-GaN heterostructure photoconductive detector†
Abstract
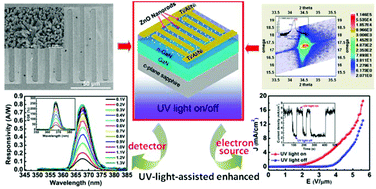
Field emission electron beam (EB) pumped AlGaN-based semiconductors are considered to be a potentially promising way to overcome the technical bottlenecks that restrict the development of AlGaN-based UV luminescence devices and realize efficient UV light sources. However, the required field emission electron sources based on nanomaterials are still inefficient due to their low field emission current density. Herein, a type of UV-light-assisted self-positive-feedback enhanced field emission electron source is proposed to develop a high-efficiency electron source which is promising for application in EB pumped AlGaN-based UV light sources that can also be generalized to deep UV (DUV) luminescence devices. The UV-light-assisted field emission source is composed of an n-GaN metal–semiconductor–metal (MSM) structure photodetector assembled with 1D ZnO nanorods by a self-assembled hydrothermal growth method, which simultaneously possesses attributes of the photoelectric effect and electron emission. The optical, photoelectric, and field emission properties are investigated in detail. The results show that the 1D ZnO nanorods/n-GaN heterostructure photodetector presents an obvious photoconductive effect. It has a peak spectral responsivity of 0.793 A W−1 at a bias voltage of 1.3 V, corresponding to an EQE higher than 267.8%, with an internal photoconductive gain reaching up to 2.51 × 103. As to the field emission properties, its turn-on electric field can be greatly reduced from 3.6 V μm−1 in the dark to 1.36 V μm−1 under UV illumination, and the field emission current density increases from lower than 3 mA cm−2 to as high as 8 mA cm−2 at an electric field of 4.5 V μm−1. The mechanism involved can be attributed to an increase of electron concentration in both the conduction bands and an increase of conduction band bending under UV illumination that reduces the effective potential barrier height of the ZnO nanorods. Through this research, an efficient field emission electron source with a self-enhancing effect is developed by combining the photoelectric effect with the electron emission process.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...