Tailoring adhesion of anionic surfaces using cationic PISA-latexes – towards tough nanocellulose materials in the wet state†
Abstract
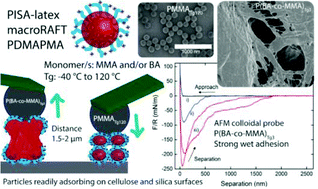
Cationic latexes with Tgs ranging between −40 °C and 120 °C were synthesised using n-butyl acrylate (BA) and/or methyl methacrylate (MMA) as the core polymers. Reversible addition–fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) combined with polymerisation-induced self-assembly (PISA) allowed for in situ chain-extension of a cationic macromolecular RAFT agent (macroRAFT) of poly(N-[3-(dimethylamino)propyl] methacrylamide) (PDMAPMA), used as stabiliser in so-called surfactant-free emulsion polymerisation. The resulting narrowly distributed nanosized latexes adsorbed readily onto silica surfaces and to model surfaces of cellulose nanofibrils, as demonstrated by quartz crystal microbalance with dissipation monitoring (QCM-D) measurements. Adsorption to anionic surfaces increased when increasing ionic strength to 10 mM, indicating the influence of the polyelectrolyte effect exerted by the corona. The polyelectrolyte corona affected the interactions in the wet state, the stability of the latex and re-dispersibility after drying. The QCM-D measurements showed that a lower Tg of the core results in a more strongly interacting adsorbed layer at the solid–liquid interface, despite a comparable adsorbed mass, indicating structural differences of the investigated latexes in the wet state. The two latexes with Tg below room temperature (i.e. PBATg-40 and P(BA-co-MMA)Tg3) exhibited film formation in the wet state, as shown by AFM colloidal probe measurements. It was observed that P(BA-co-MMA)Tg3 latex resulted in the largest pull-off force, above 200 m Nm−1 after 120 s in contact. The strongest wet adhesion was achieved with PDMAPMA-stabilized latexes soft enough to allow for interparticle diffusion of polymer chains, and stiff enough to create a strong adhesive joint. Fundamental understanding of interfacial properties of latexes and cellulose enables controlled and predictive strategies to produce strong and tough materials with high nanocellulose content, both in the wet and dry state.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...