Self-assembly dynamics and antimicrobial activity of all l- and d-amino acid enantiomers of a designer peptide†
Abstract
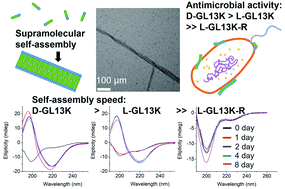
Recent studies have shown that antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) can self-assemble into supramolecular structures, but this has been overlooked as causative of their antimicrobial activity. Also, the higher antimicrobial potency of D-enantiomers compared to L-enantiomers of AMPs cannot always be attributed to their different resistance to protease degradation. Here, we tested all L- and D-amino acid versions of GL13K, an AMP derived from a human protein, to study structural links between the AMP secondary structure, supramolecular self-assembly dynamics, and antimicrobial activity. pH dependence and the evolution of secondary structures were related to a self-assembly process with differences among these AMPs. The two GL13K enantiomers formed analogous self-assembled twisted nanoribbon structures, but D-GL13K initiated self-assembly faster and had notably higher antimicrobial potency than L-GL13K. A non-antimicrobial scrambled amino acid version of L-GL13K assembled at a much higher pH to form distinctively different self-assembled structures than L-GL13K. Our results support a functional relationship between the AMP self-assembly and their antimicrobial activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...