Selective bilirubin sensor fabrication based on doped IAO nanorods for environmental remediation
Abstract
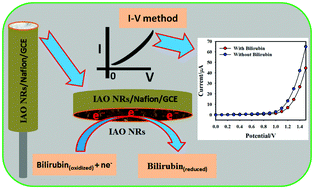
In this approach, low-dimensional facile iron-doped antimony oxide nanorods (IAO NRs) were prepared using the hydrothermal technique in basic medium. The optical, morphological, and structural properties of the IAO NRs were systematically characterized by the FTIR, UV/vis, FE-SEM, TEM, EDS, XPS, and XRD techniques. A glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was modified with a thin-layer of IAO NRs using Nafion as a conducting binder to fabricate an ultra-sensitive bilirubin (BR) sensor at room conditions. Herein, BR was selected as the target analyte from a selectivity study using eleven analytes. The electrochemical performance of the proposed BR sensor was studied by electrochemical approaches and the obtained results showed higher sensitivity, a large dynamic range and long-term stability towards selective BR in a phosphate buffer phase. A linear calibration plot was obtained for a wide-ranging linear dynamic range (LDR) of bilirubin concentration (0.1 nM–0.01 M) and the limit of detection (LOD) value was obtained as 16.5 ± 0.05 pM by considering a signal-to-noise ratio of 3. The sensitivity value was calculated as 2.347 μA μM−1 cm−2 from the calibration plot. It is an efficient approach to develop a non-enzymatic biosensor based on a low dimensional facile IAO NR coated GCE probe using the electrochemical reduction phenomenon.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...