Heterojunction Cu2O/RGO/BiVO4 ternary nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activities towards degradation of rhodamine B and tetracycline hydrochloride†
Abstract
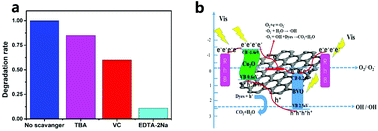
Compared to the traditional type II heterojunction photocatalyst (Cu2O/BiVO4), bulk BiVO4 was modified in this study by reduced graphene oxide (RGO) with a Schottky structure to optimize the coupling interface of BiVO4. Cu2O nanoparticles were then grown in situ on the RGO/BiVO4 surface to yield a heterojunction structure with an internal electric field, allowing movement of photogenerated electrons and holes in opposite directions to participate in redox reactions. The as-obtained optimized Cu2O/RGO/BiVO4 material exhibited excellent photocatalytic degradation performance towards organic pollutants. The reaction rate constant of rhodamine B (RhB) was estimated as 0.0324 min−1, which was almost 5.94, 5.15 and 1.94-fold higher than those of bare BiVO4, 4%RGO/BiVO4 and 5%Cu2O/BiVO4, respectively. Moreover, the optimized material displayed good activity in the degradation of the colorless organic contaminant tetracycline hydrochloride (TC). The reaction rate constant was estimated as 0.0219 min−1, which was almost 1.6-, 1.4- and 1.63-fold higher than those of bare BiVO4, 4%RGO/BiVO4 and 5%Cu2O/BiVO4, respectively. The hole and superoxide radical worked as active species for degradation of organic matter. Such a significant increase in degradation efficiencies was attributed not only to the formation of a heterojunction structure but also to rapid electron transfer between interfaces.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...