A long-cycle and high-rate Si/SiOx/nitrogen-doped carbon composite as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries†
Abstract
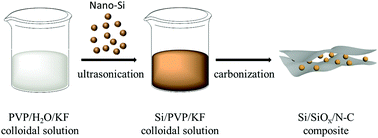
Silicon (Si) is proposed as a promising anode material for high-performance lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) due to its ultrahigh theoretical capacity. However, this material suffers from serious volume expansion during lithium insertion and extraction processes and even severe pulverization, so the practical commercial application of Si electrode materials still faces numerous challenges. Herein, the natural polymer konjac flour (KF) and polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) are used as the carbon source and the nitrogen source, respectively, to synthesize Si/SiOx/N–C composites by a scalable sol–gel method and one-step pyrolysis. Benefiting from the strong interfacial adhesion between the Si/SiOx nanoparticles and KF, the Si/SiOx nanoparticles are well embedded into the nitrogen-doped carbon layers after carbonization. Moreover, the SiOx buffer layers can effectively alleviate the volume change of Si during the cycling process. As an anode material for LIBs, the Si/SiOx/N–C composite exhibits an outstanding cycling performance (952 mA h g−1 after 100th cycles at 200 mA g−1) and a high capacity retention ratio (91.7%). These results suggest that this superior anode material synthesized by a simple and scalable method has potential application in LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...