A magnetic activated sludge for Cu(ii) and Cd(ii) removal: adsorption performance and mechanism studies
Abstract
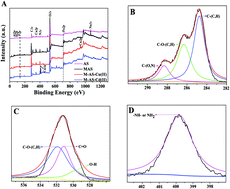
In the present study, a novel magnetic activated sludge (MAS) was successfully synthesized and applied for heavy metal removal. The MAS was characterized by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), zeta potential analysis, X-ray diffraction (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The optimum sorption conditions were identified in view of different adsorbents, adsorbent dosages, pH values and contact times. The batch experiment implied that the pseudo-second-order model was better to describe the adsorption kinetics of Cu(II) and Cd(II) onto the MAS. The adsorption levels of Cu(II) and Cd(II) onto the MAS were in accordance with the Langmuir isotherm with maximum adsorption capacities of 72.1 and 71.3 mg g−1, respectively. According to XPS analysis, the metal sorption process was mainly caused by surface complexation, electrostatic attraction and precipitation. After four desorption cycles using Na2EDTA, the removal efficiencies of Cu(II) and Cd(II) decreased to 88.2% and 87.1%, respectively. The experimental result illustrated that the MAS could be an economical adsorbent for actual heavy metal contaminated wastewater treatment.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...