Flame-retardant and smoke-suppressing wood obtained by the in situ growth of a hydrotalcite-like compound on the inner surfaces of vessels†
Abstract
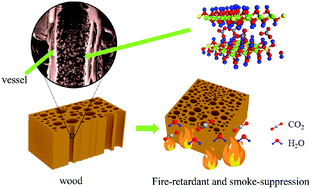
The shortcomings of traditional inorganic flame retardants for wood, such as how easily they fall off and how they change the natural attributes of wood, hinder their practical usage severely. In this work, a novel flame retarding technique was developed for wood (paulownia wood) through the in situ hydrothermal growth of a hydrotalcite-like compound (MgAl layered double hydroxide, MgAl-LDH) on the inner surfaces of vessels. MgAl-LDH nanosheets were uniformly grown on the inner surfaces of the wood vessels to form spherical aggregates with sizes of about 0.5 to 1 μm. The in situ grown MgAl-LDH sheets in the wood vessels prevented flame combustion and smoke diffusion; this was confirmed from limiting oxygen index (LOI) and the cone calorimeter tests. The results indicated that the LOI of the wood increased from 19 to 48% after the growth of the LDH. The total heat release decreased by 66.17%, and the total smoke production decreased by 77.57%. Mechanical property tests proved that the in situ growth of MgAl-LDH resulted in the wood showing enhanced tensile strength and compressive strength. Obviously, this low cost and efficient method can be used to improve the flame retardancy and smoke suppression of wood without changing its appearance and structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...