Bimetallic MOF-derived porous CoNi/C nanocomposites with ultra-wide band microwave absorption properties
Abstract
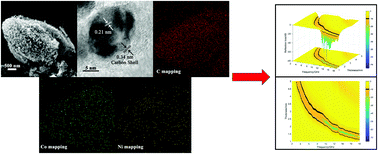
In this paper, we report the facile synthesis of CoNi/C nanocomposites derived from bimetallic metal organic frameworks for electromagnetic wave absorption applications. The effects of carbonation temperature on the phase structure, morphology and microwave absorption properties of the derived nanocomposites were thoroughly studied. Micro-structure characterization results indicated that the obtained CoNi/C composites are composed of numerous fine particles with the size of 20 nm, and in the composites, Ni, Co, and C elements are uniformly distributed. Electromagnetic wave absorption property evaluation showed that CoNi/C obtained at 650 °C outperformed those samples prepared at 500, 800 or 950 °C. The minimum reflection loss (RL) of −74.7 dB could be achieved with a thickness of 1.8 mm at 15.6 GHz. The effective absorption bandwidth (RL ≤ −10 dB) ranged from 2.9 GHz to 18 GHz. This study shows that these porous Co–Ni/C nanocomposites derived from MOFs are attractive candidates as electromagnetic (EM) wave absorbers due to the combined advantages of excellent impedance matching and strong interfacial loss between metallic NPs and porous carbon composites.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...