A dual-excitation fluorescent probe EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT) for hydrazine detection in aqueous solutions and living cells
Abstract
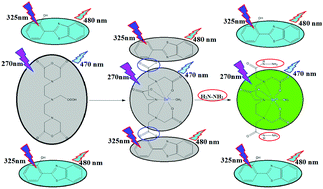
Based on the esterification of 2-(2-hydroxyphenyl)benzothiazole (HBT) and a rare-earth metal ion complex EuIII-dtpa, a novel dual-excitation fluorescence probe, EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT), was developed for the detection of hydrazine (N2H4). The structure of dtpa-bis(HBT) was characterized via FT-IR and NMR, and its optical properties were studied via UV-vis absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy. Influencing factors including solution acidity, interfering substances and N2H4 concentrations were considered for the detection of N2H4 using EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT). EuIII-dtpa-bis(N2H4) and HBT emit significant fluorescence at 470 nm (λex = 270 nm) and 480 nm (λex = 325 nm), respectively. The detection limit of EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT) with N2H4 was 0.283 μM (14 ppb) and 0.182 μM (9 ppb) upon excitation at 270 nm and 325 nm, which is close to and lower than the EPA standard (10 ppb), respectively. The mechanism for the detection of N2H4 by EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT) was deduced from the experimental results and theoretical calculations. Also, cytotoxicity and cell imaging experiments of EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT) were performed. The experimental results showed that the fluorescent probe EuIII-dtpa-bis(HBT) can be applied to detect N2H4 in aqueous solution and living cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...