Hydrophilic encapsulation of reduced graphite oxide (r-GO) by admicellar polymerization for application in biosensors
Abstract
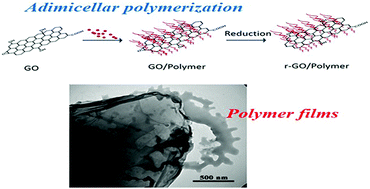
Herein, hydrophilic encapsulation of reduced graphite oxide (r-GO) was achieved by admicellar polymerization. Functional polymer thin films were coated on the r-GO surface for enhancing the water dispersion of r-GO. The morphology was observed by TEM and SEM. Moreover, a PHEMA thin film was coated on the surface of r-GO by admicellar polymerization using a surfactant at low concentration. The percentage of the film coated on r-GO was calculated to be 40 wt% by thermal analysis. FT-Raman has been applied to illustrate that admicellar polymerization is a nondestructive functionalization method. The water contact angles decreased from 105° to 63° after admicellar polymerization; this indicated the successful hydrophilic encapsulation of r-GO. Moreover, r-GO/PHEMA-modified glassy carbon (r-GO/PHEMA/GC) functioned well as an electrochemical biosensor for the detection of hemopexin-like domain of matrix metalloproteinase 14 (PEX-14).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...