Solubilization and interaction of ciprofloxacin with pluronics and their mixed micelles†
Abstract
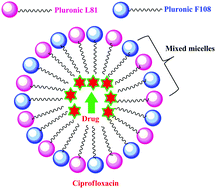
Ciprofloxacin is preferred to be used in acidic medium because of its poor solubilisation in neutral medium. To observe the solubilisation of ciprofloxacin in neutral medium through a pluronic mixed micellar system this study was undertaken. A binary mixture comprising Pluronic F108 and Pluronic L81 has been utilized to observe the solubility of ciprofloxacin compared to the solubility in single pluronics. With the selected ratio of surfactants a mixed pluronic was prepared and was employed for all the characterization studies. The interaction of the drug ciprofloxacin with the chosen combination of mixed pluronics was analysed by UV-visible spectrophotometry, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), dynamic light scattering (DLS), rheology, fluorescence spectrophotometry, zeta potential measurements and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) analysis. The partition coefficient of the mixed pluronic was also calculated and found to be 23.4 compared to the partition coefficient values of the single pluronics, 13.4 and 8.4, repectively. The UV-visible spectrum of the mixed micelle–drug system showed an intermediate absorbance value compared to the single micelle–drug systems. The FT-IR spectra suggested strong bonding taking place in the mixed pluronic–drug system. Addition of sodium chloride doesn’t increase the encapsulation efficiency of the mixed pluronic with the drug as seen from dynamic light scattering studies. Fluorescence spectral studies indicated the formation of excimers. The rheological parameters suggested that the mixed pluronic system had a more stable complex with the drug and sodium chloride. The results demonstrated that the particular combination of mixed pluronics had a profound effect on the solubilisation of the drug. This is probably the first report of solubilisation of ciprofloxacin in a mixed micellar system.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...