In silico study of 3-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4-diones as inhibitors of HIV RT-associated RNase H using molecular docking, molecular dynamics, 3D-QSAR, and pharmacophore models
Abstract
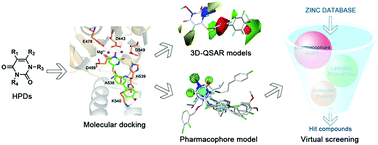
HIV reverse transcriptase (RT)-associated ribonuclease H (RNase H) plays an important role in HIV multiplication and represents a novel anti-HIV target. Recently, a novel series of 3-hydroxypyrimidine-2,4-dione (HPD) derivatives have been reported as potent inhibitors of HIV RT-associated RNase H; they also exhibit antiviral activities, with EC50 values in the low micromolar range. To better understand their structure–activity relationships and mechanisms of action, an integrated computational study, including molecular docking, molecular dynamics (MD), three-dimensional quantitative structure–activity relationship (3D-QSAR), and pharmacophore modeling, was performed on these HPDs. Ninety-three HPDs were firstly docked into the RNase H active site; then, MD simulations were performed to validate the accuracy of the docking results. The comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) methods were used to generate 3D-QSAR models. Structure-based CoMFA (q2 = 0.908, R2 = 0.978, rpred2 = 0.949) and CoMSIA (q2 = 0.908, R2 = 0.960, rpred2 = 0.919) models and docking-based CoMFA (q2 = 0.832, R2 = 0.985, rpred2 = 0.967) and CoMSIA (q2 = 0.927, R2 = 0.990, rpred2 = 0.977) models were constructed and exhibited excellent predictive ability. The generated pharmacophore model provided deep insight into the pharmacological structural characteristics of the HPDs. Nine virtually screened compounds and six newly designed compounds based on the pharmacophore and 3D-QSAR models are potential leads of HIV RNase H inhibitors. These results may provide important information for the design and development of potent and novel HIV RNase H inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...