Multifunctional nanocarriers based on graphitic-C3N4 quantum dots for tumor-targeted, traceable and pH-responsive drug delivery†
Abstract
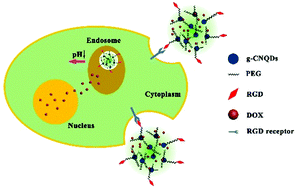
Considering the intrinsic complexity of cancer, the emergence of multifunctional nanocarriers provides more possibilities for cancer therapy. Herein, a novel multifunctional nanocarrier (g-CNQDs–PEG–RGD) is successfully developed by covalently grafting graphitic-C3N4 quantum dots (g-CNQDs) with arginine–glycine–aspartic acid (RGD) via diamine-terminated oligomeric polyethylene glycol (PEG). The functionalization of g-CNQDs with PEG and RGD imparts the nanocomposite with low cytotoxicity, excellent physiological stability and specific targeting ability toward cancer cells with the αvβ3 receptor. The widely used fluorescent antineoplastic anthracycline drug doxorubicin (DOX) is non-covalently loaded onto g-CNQDs–PEG–RGD. It is advantageous that the g-CNQDs–PEG–RGD–DOX nano-assembly exhibits enhanced cellular uptake by HepG2 cells, which overexpress integrin αvβ3 receptors. Thus, the enhanced targeting specificity and intracellular acid condition-triggered drug release promise excellent therapeutic effects. Meanwhile, the inherent stable fluorescence of g-CNQDs–PEG–RGD and DOX enables real-time monitoring of cellular uptake of the g-CNQDs–PEG–RGD–DOX nano-assembly, consequent release of DOX and the fate of the carrier. These findings demonstrate that g-CNQDs–PEG–RGD–DOX will be promising for high treatment efficacy with minimal side effects in future therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...