Multifunctional dual-mesoporous silica nanoparticles loaded with a protein and dual antitumor drugs as a targeted delivery system†
Abstract
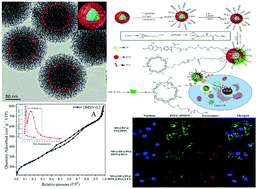
Herein, dual-mesoporous structure silica (with pore sizes from 2 to 4 nm and from 4 to 16 nm) simultaneously modified with amino and carboxyl groups was successfully synthesized. Doxorubicin (DOX) and cisplatin (Pt) were loaded onto the interior of the spherical mesoporous silica carrier material, and the macromolecular model drug bovine serum albumin (BSA) was loaded onto the outer layer using aminoguanidine-cyclodextrin as a blocking agent; moreover, folic acid (FA) was introduced to achieve targeted functionalization. Thus, a multi-drug and protein therapy system was constructed with a targeting functionality and pH stimulation-responsive controlled release system. Drug-loaded testing results showed that the amino and carboxyl-functionalized nanoparticles displayed high degrees of drug loading for DOX, Pt and BSA. The loading rate of BSA reached 33%. In vitro drug release experiments confirmed that this drug carrier system could achieve “zero pre-release”. The cytotoxicity of the dual-drug system was significantly higher than those of the single-load drug delivery systems although it decreased the toxicity of the drug itself towards the HeLa cells. The multi-drug and protein therapy system with targeting functionality showed better synergistic targeted therapeutic effects for HeLa cells. All the experiments show that the combination of multi-drugs and protein is a promising strategy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...