Water-soluble diboronic acid-based fluorescent sensors recognizing d-sorbitol†
Abstract
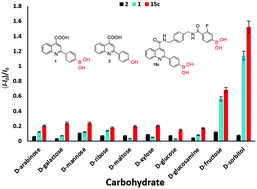
Herein, several boronic acid-based sensors were reported selectively recognizing D-sorbitol in aqueous solution. The fluorescence of sensor 15c was enhanced by 1.5-fold when combined with a low concentration of D-sorbitol (8.88 μM), and the fluorescence enhanced by 0.6-fold after binding to D-fructose, while it did not change obviously when combined with other carbohydrates, including D-arabinose, D-galactose, D-mannose, D-ribose, D-maltose, D-xylose, D-glucose and D-glucosamine. Fluorescence tests were carried out in DMSO/PBS (pH 9, 0.1 M) solution (1 : 99, v/v), at room temperature, which indicated that the sensors are water-soluble. In addition, competition studies showed that sensor 15c works well as a D-sorbitol-specific fluorescence sensor in both the absence and presence of carbohydrate interferents. And sensor 15c has a high binding constant (10 922 ± 776 M−1) and a low limit of detection (6.91 × 10−7 M) at pH 9 among the investigated sensors toward D-sorbitol. Furthermore, sensor 15c was applied to the analysis of real samples (D-sorbitol for oral administration). These studies indicated that sensor 15c may serve as a potential tool to detect the content of D-sorbitol in drugs and food products.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...