Virtual screening and experimental validation of eEF2K inhibitors by combining homology modeling, QSAR and molecular docking from FDA approved drugs
Abstract
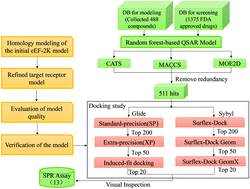
Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF2K), a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase, is a potential target for treating cancer. eEF2K can reduce the binding ability of eEF2 to ribosomes by phosphorylating eEF2, thereby inhibiting peptide chain extension and negatively regulating protein synthesis, which provides a cytoprotective mechanism for the development of cancer. eEF2K has been reported to be overexpressed in various types of cancers. Therefore, it is of high importance to discover new eEF2K inhibitors for cancer therapy. Here, we proposed a three-step screening strategy to seek eEF2K inhibitors from the FDA approved drug library: homology modeling of eEF2K protein, SAR-based virtual screening, and docking-based virtual screening. Based on the screening strategy, 13 drugs with high evaluation scores were purchased to measure their binding affinity (KD) to eEF2K by using the SPR assay. The assay results suggested that 4 drugs may be potential eEF2K inhibitors, which are Pemetrexed (KD = 0.104 μM), Entecavir (KD = 2.16 μM), calcium levofolinate (KD = 11.7 μM), and Fosbretabulin (KD = 34.5 μM). To further validate whether these drugs act on eEF2K, Western blot (WB) analysis was performed, which showed that Pemetrexed and Entecavir could inhibit the eEF2K activity. Furthermore, molecular dynamics (MD) simulation was carried out to further demonstrate the interaction of eEF2K with Pemetrexed, the most bioactive drug. The specific in vitro/in vivo interaction mechanisms between these drugs and eEF2K are under investigation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...