Photochemical oxidation of water catalysed by cyclometalated Ir(iii) complexes bearing Schiff-base ligands†
Abstract
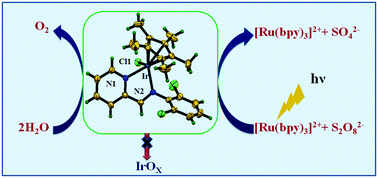
Synthesis, characterization and photochemical water oxidation activity of three cyclometalated Ir(III) complexes, [(η5-C5Me5)Ir(L1)Cl]PF6 (1), [(η5-C5Me5)Ir(L2)Cl]PF6 (2) and [(η5-C5Me5)Ir(L3)Cl]PF6 (3) (where, L1 = N-(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)aniline, L2 = 2,6-diisopropyl-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)aniline) and L3 = 2,6-dichloro-N-(pyridin-2-ylmethylene)aniline) is reported. The molecular structures of complexes 2 and 3 were determined by single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. Catalytic investigations of 1–3 for visible light-driven photochemical oxidation of water carried out in the presence of Na2S2O8 as a sacrificial oxidant and [Ru(bpy)3]2+ as a photosensitizer showed good water oxidation activity of the complexes. Interestingly, the rate of O2 evolution follows the trend 3 > 1 > 2 with complex 3 containing a (–Cl) substituent on the N,N′ ligand (L3) showing higher activity than that of 1 with an unsubstituted ligand (L1) followed by 2 containing (–iPr) groups on the ancillary ligand (L2). Furthermore, the complexes showed good stability and no degradation was observed during the photocatalytic water oxidation reactions. Thus the influence of ancillary ligands on the photochemical water oxidation activity of cyclometallated Ir(III) complexes containing substituted Schiff-base ligands is demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...