Multiplexed electrochemical and SERS dual-mode detection of stroke biomarkers: rapid screening with high sensitivity†
Abstract
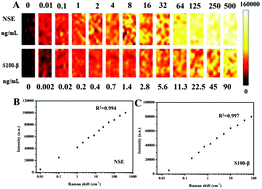
In this work, a real-time assay for a highly sensitive, label-free, multiplexed electrochemical and surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopic (SERS) detection of stroke biomarkers by neuron-specific enolase (NSE) and S100-β protein was developed using lateral flow devices. We found two kinds of Raman dye (Nile blue A (NBA) and 4-mercaptobenzoic acid (4-MBA))-decorated Au@AgNPs, which show both strong SERS signals and electrochemical redox characteristic peaks. The lateral flow assays are performed by a two-biomarker method for the first time. A sandwich structure contains the Raman dye-labeled Au@AgNPs with the first antibody, the second antibody immobilized on the lateral flow assay biosensor, and the target antigens. Thus, in the presence of the target antigens, the Raman dye-labeled Au@AgNPs could be bonded to the modified lateral flow device surface by antibody–antigen–antibody interactions. As a result, a simultaneous immunoassay for NSE and S100-β based on multiple labels is developed using electrochemical and SERS immunoassays. The prepared immunoassay biosensor for the detection of NSE and S100-β shows high sensitivity, selectivity, low detection limit and long-term stability. Compared with different Raman signals and electrochemical characteristic peaks, this has the lowest detectable concentration for NSE and S100-β at a signal to noise ratio of 3. The proposed immunosensor can be applied to determine NSE and S100-β in human blood serum. In addition, the electrochemical and SERS immunosensor has potential applications in the diagnosis and treatment of strokes in the field of clinical research.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...