Highly biocompatible zwitterionic dendrimer-encapsulated platinum nanoparticles for sensitive detection of glucose in complex medium
Abstract
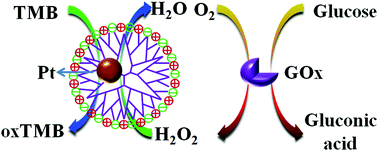
The development of ultra-small platinum nanoparticles is very important for the sensitive detection of glucose in complex medium without protein interference. Zwitterionic dendrimer-encapsulated platinum nanoparticles (Ptn-G5MC NPs) have been developed and studied for the highly sensitive and selective colorimetric detection of glucose. Firstly, zwitterionic dendrimer (G5MC) was obtained by surface modification of generation 5 poly(amidoamine) dendrimer with maleic anhydride and cysteamine. The calculated average diameters of Pt nanoparticles (Pt NPs) for Ptn-G5MC (n = 55, 110, and 165) were 1.64 ± 0.22, 2.09 ± 0.24, and 2.98 ± 0.29 nm, respectively. Ptn-G5MC NPs not only had high stability in various pH solutions and fibrinogen solutions, but also showed no noticeable cytotoxicity against HUVEC cells and HeLa cells. In addition, Ptn-G5MC NPs catalyzed oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) with H2O2 to generate blue oxidized TMB (oxTMB), indicating their peroxidase-like property. This peroxidase-like reaction followed a typical Michaelis–Menten kinetics. Furthermore, this colorimetric reaction was used for glucose detection with high sensitivity and selectivity. The linear range of glucose concentration with absorbance at 652 nm was from 7 to 1380 μM, and the detection limit was 2.8 μM. More importantly, the relative activity of Ptn-G5MC NPs was not affected by proteins. These enhanced properties are attributed to the ultra-small size of Pt NPs and high stability of Pt55-G5MC NPs in complex medium. The glucose concentration in saliva as a real sample was found to be 0.18 mM. The proposed glucose sensor could have promising applications for glucose detection in biocatalysis and bioassays in the future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...