New insights into the binding behavior of lomefloxacin and human hemoglobin using biophysical techniques: binary and ternary approaches
Abstract
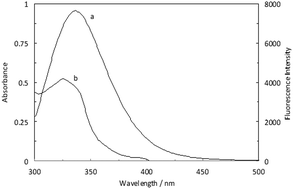
The interaction of hemoglobin (Hb) with lomefloxacin (LMF), in the absence and presence of norfloxacin (NRF) functioning as a binary and ternary system, has been analyzed through the utilization of different spectroscopic and molecular dynamics (MD) simulation techniques. The thermodynamic parameters have been calculated from the fluorescence data that were measured at three different temperatures. Considering the negative values of ΔH0 and ΔS0, it is indicated that the functionalities of van der Waals forces and hydrogen bonds are essential throughout the binding of LMF and NRF to Hb. The fluorescence spectra study of Hb, with regards to the binary and ternary systems, indicated that the fluorescence intensity decreased as a result of the drug enhancement, which proves that the interaction has occurred. The existing distance I between the donor and acceptor was gained using the Förster energy, which was in accordance with the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) and found to be 2.33 and 2.39 nm for the Hb–LMF and (Hb–NRF) LMF complexes, respectively. These numbers are indicative of the induced complex formation between Hb and the drugs in both systems. The properties of the Tyr and Trp residues were obtained through synchronous fluorescence results, the complex structure of Hb–LMF was observed to be altered in the absence and presence of NRF. The outcomes of circular dichroism (CD) represented the conformational changes of Hb that had occurred upon binding to LMF and NRF as the binary and ternary systems. Moreover, molecular modeling confirmed the experimental results which were obtained with regards to the binding of the Hb–LMF and (Hb–NRF) LMF complexes. The crucial functionality of the polar residues in the stability of the complexes was indicated by the interaction studies of LMF in the binary and ternary systems.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...