Determination of the DNA binding properties of a novel PARP inhibitor MK-4827 with calf-thymus DNA by molecular simulations and detailed spectroscopic investigations†
Abstract
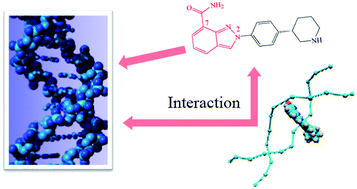
The binding interaction of niraparib (MK-4827), a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, with calf thymus deoxyribonucleic acid (ctDNA) has been explored by various theoretical and experimental techniques. Molecular docking models predicted that all the binding conformations of MK-4827 interaction with DNA are clustered into two types: one intercalates into the middle part of the DNA composed of A–T base pairs, and the other one binds with the bottom part of the DNA composed of C–G base pairs. Molecular dynamics simulations further concluded that MK-4827 could steadily intercalate the A–T base pairs of the DNA structure, and the hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic forces help maintain this combination. Fluorescence titration of MK-4827 by ctDNA indicated that the interaction involves static quenching, which resulted from the temperature dependence of the MK-4827–ctDNA complex and was further verified by fluorescence lifetime experiments. Iodide quenching, DNA melting, viscosity and fluorescence competitive experiments with two known intercalative binders confirmed that intercalation is the main DNA binding mode for MK-4827 and has certain influence on the conformation of the ctDNA as indicated by CD.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...