Synthesis, characterization and computational study of an ilmenite-structured Ni3Mn3Ti6O18 thin film photoanode for solar water splitting†
Abstract
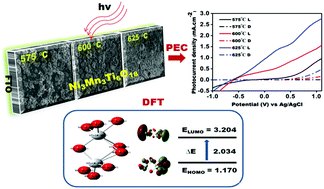
Ilmenite-structured Ni3Mn3Ti6O18 solid solution thin films have been deposited on FTO glass substrates by aerosol-assisted chemical vapor deposition (AACVD) using a 1 : 1 : 2 homogenous mixture of nickel(II) acetate monohydrate (Ni(CH3COO)2·H2O), anhydrous manganese(II) acetate (Mn(CH3COO)2) and titanium(IV) butoxide (Ti(O(CH2)3CH3)4) in the presence of trifluoroacetic acid (TFA) using tetrahydrofuran (THF) as a solvent. Thin films prepared at 575, 600 and 625 °C were characterized by powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM), energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), FT-Raman and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), which demonstrated the development of single phase hexagonal microspherical objects of Ni3Mn3Ti6O18 clusters with precise stoichiometry. A direct optical band gap energy of 2.42, 2.06, and 1.70 eV for thin films fabricated at 575, 600, and 625 °C, respectively, was estimated by UV-vis spectrophotometry. The Ni3Mn3Ti6O18 photoanode deposited at 625 °C for 45 minutes yielded a photocurrent density of 2.05 mA cm−2 at +0.7 V vs. Ag/AgCl/3 M KCl using a 0.5 M NaOH electrolyte under AM 1.5 G illumination (100 mW cm−2) as compared to the films grown at 575 and 600 °C and studied under similar conditions. The charge transfer dynamics of the thin films were also explored using the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technique. The Mullikan charge population calculated through density functional theory (DFT) studies carried out at the B3LYP 6-31G(d,p) level for the [Ti2O6]4− unit of ilmenite determined the highest negative charge on the O atom. The frontier molecular orbital energies (EHOMO and ELUMO) and natural bond orbital (NBO) analysis gave a band gap value of 2.03 eV, complementing the experimental results. Band structure analysis of the [Ti2O6]4− slab showed that the valence band and conduction band are comprised of O 2s, O 2p and Ti 3d orbitals. The results of the present investigation point towards the possibility of an ilmenite form of transition metal oxides as a potential broad spectrum visible light absorbing photocatalyst for solar driven water splitting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...