Preparation and properties of ZnO/sodium alginate bi-layered hydrogel films as novel wound dressings
Abstract
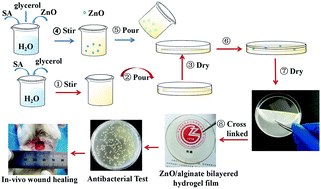
As one kind of natural material, alginate has been widely investigated and used in the biomedical field. Alginate-based hydrogels with the desired functional performance and good water-maintaining ability are helpful to promote the development of wound dressings. In this work, zinc oxide/sodium alginate (ZnO/SA) bi-layered hydrogel films were designed and prepared using ZnO and SA as the raw materials by a strategy combining casting and solvent evaporation processes. The chemical structure and porous morphology of the prepared hydrogel films were determined by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, X-ray diffraction, thermogravimetry and field-emission scanning electron microscopy. Furthermore, some properties of the bi-layered hydrogel films were also evaluated regarding the wettability, water solubility, swelling ability, mechanical properties, antibacterial properties, in vitro cytotoxicity and in vivo wound healing ability. The results suggest that the prepared ZnO/SA bi-layered hydrogel films have high transparency, suitable hygroscopicity, good swelling and adequate mechanical strength. With improving the content of ZnO, the trend of the antibacterial rate of the ZnO/SA films increases gradually and a maximum antibacterial rate of 68.4% can be achieved when the content of ZnO is 0.04%. In addition, the ZnO/SA bi-layered hydrogel films have no significant cytotoxicity to L929 fibroblast cells through a MTT assay, and also possess enhanced in vivo wound healing ability, presenting promising potential for application as novel wound dressings.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...