Spectrophotometric and photocatalytic studies of H-bonded charge transfer complex of oxalic acid with imidazole: single crystal XRD, experimental and DFT/TD-DFT studies†
Abstract
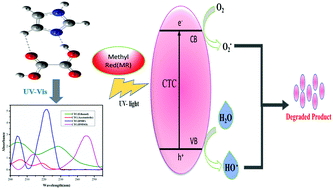
Apart from traditional work, we present here a new idea for an intermolecular interaction between an organic acceptor (oxalic acid, OX) and imidazole donor (IZ) to synthesize a charge transfer complex (CTC), which acts as an efficient photocatalyst compared to its reactants. The photocatalytic activity of the complex was adequately tested under UV light, which indicated significant degradation of the methyl red (MR). Cyclic voltammetry has been carried out to study the redox processes and chemical oxygen demand (COD) data are provided. Nowadays, CT interactions have drawn interest because of their crucial role in charge separation. This examination began with spectrophotometric studies to understand the formation of a CT complex that connected through N+–H⋯O− hydrogen bonding, its structure was confirmed by X-ray single crystal spectroscopy and its various thermodynamic parameters have been estimated. TGA–DTA studies reveal that the complex is highly stable which favors DNA binding as evidenced by a docking study. Molecular docking analysis shows the best binding site of DNA with the CT complex, which binds efficiently with a free energy of binding (FEB) value of −159.47 ± 8 kcal mol−1. Theoretical calculations have been performed on the present complex and its constituents using density functional theory (DFT). The band gap energy from the HOMO to the LUMO, ΔE = 5.38 ± 0.05 eV was obtained by theoretical calculations (B3LYP/6-311++G(d,p) level) from the frontier molecular orbital energies and the results obtained are utilized to define structure based molecular properties of the studied complex. The differences between the observed vibrational bands of the complex and its constituents, for particular functional groups i.e. C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) O, O–H, N–H and C–H participating in H-bond formation, affirm the formation of the present complex. The newly designed complex was analyzed in both the solid and liquid states by FTIR, 1H NMR, UV–visible spectroscopy and PXRD. In order to get an understanding of the level of accuracy, the root mean square error (RMSE) is estimated for bond lengths, bond angles and harmonic and scaled vibrational frequencies which are 0.026 Å, 1.852°, 195 cm−1 and 134 cm−1, respectively.
O, O–H, N–H and C–H participating in H-bond formation, affirm the formation of the present complex. The newly designed complex was analyzed in both the solid and liquid states by FTIR, 1H NMR, UV–visible spectroscopy and PXRD. In order to get an understanding of the level of accuracy, the root mean square error (RMSE) is estimated for bond lengths, bond angles and harmonic and scaled vibrational frequencies which are 0.026 Å, 1.852°, 195 cm−1 and 134 cm−1, respectively.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...