Gallic acid influence on bovine serum albumin thermal stability†
Abstract
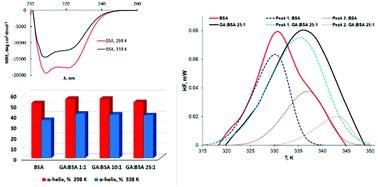
Gallic acid (GA) is a naturally occurring plant phenolic acid with moderate affinity for BSA, but its presence in different concentrations may change the thermal stability of the protein. The present study explores the effect of GA on the thermal denaturation of bovine serum albumin (BSA) using calorimetric and spectroscopic tools. Differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and circular dichroism spectroscopy (CD) results indicated that GA binding increased the protein intramolecular packing and induced higher thermal stability. Turbidity variations over time proved that GA binding promotes aggregation of a BSA fraction, partially unfolded by the thermal treatment. Dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements pointed to a protective effect of GA for the monomeric form of the protein coupled with enhancing large size aggregate formation. This dual effect of GA is reported for the first time in the present study. The obtained results contain significant information concerning the thermal behavior of the GA–BSA system. They offer a fresh insight into the designing of new compounds with potential inhibitor activity on protein aggregation, with applications in life sciences.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...