Design and functionalization of bioactive benzoxazines. An unexpected ortho-substitution effect†
Abstract
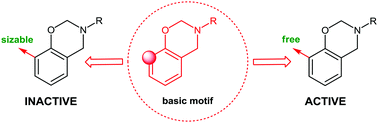
A family of o, p- and N-functionalized dihydro-2H-benzo-1,3-oxazines was synthesized and characterized. In vitro antimicrobial activity of the new benzoxazines was assessed against pathogenic fungi and Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. The screened compounds showed significant in vitro antimicrobial effect, but introduction of the bulky substituent in the ortho position of the aryl ring caused a loss of their antibacterial efficacy. Cytotoxic assay results revealed that a molecule containing long alkyl chain substituents offered a remarkable viability of mouse fibroblast cells. Additionally, the liquid nature of alkyl-chain-modified monomers and the high processing windows indicate their high application potential.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...