Surface quaternized nanosensor as a one-arrow-two-hawks approach for fluorescence turn “on–off–on” bifunctional sensing and antibacterial activity†
Abstract
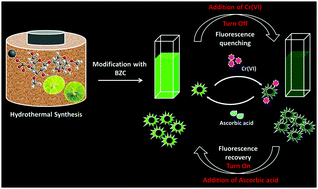
In this study, facile hydrothermal synthesis of carbon dots was developed from seaweed-derived κ-carrageenan and lemon juice followed by surface quaternization with benzalkonium chloride for the first time to improve fluorescence properties. The as-prepared spherical carbon dots (KLBC-dots) exhibited excellent water solubility, significant upconversion photoluminescence and excellent photostability. We report small angle neutron scattering (SANS) experiments with the C-dots which illustrate their surface fractals and the proneness of the C-dots to coalescence before and after surface passivation. Selective monitoring of aquatic chromium is critically significant owing to its severe toxic and carcinogenic properties, which have a dramatic impact on health and the environment. It is a remarkable fact that these KLBC-dots can serve as an “on–off–on” fluorescent platform for the selective sensing of Cr(VI) based on the inner filter effect (IFE). Ascorbic acid was employed to validate the “off–on” type fluorescent probe. Using this phenomenon, a logic gate based on the novel KLBC-dots has been constructed. This bifunctional nanosensor affords a very low detection limit (7 nM) and has the obvious benefits of rapid response, simplicity, convenience, high sensitivity and selectivity in practical applications. In addition, these carbon dots showed intracellular Cr(VI) detection and interesting antibacterial activity towards the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli. This study delivers multifunctional applications of KLBC-dots, as an antibacterial agent and for Cr(VI) detection, in environmental fields.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...