Synthesis of helical poly(phenylacetylene) derivatives bearing diastereomeric pendants for enantioseparation by HPLC†
Abstract
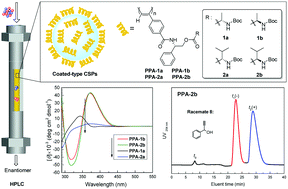
A series of novel phenylacetylene derivatives with two chiral centers, one of which was derived from L-phenylglycinol and the other from L- and D-alanine or L- and D-valine, were synthesized and polymerized in THF using Rh(nbd)BPh4 as a catalyst to obtain the corresponding stereoregular one-handed helical poly(phenylacetylene) derivatives (PPA-1a, PPA-1b, PPA-2a and PPA-2b). The polymers were used as chiral stationary phases (CSPs) in HPLC, and the effects of the coating solvents and configuration of the second amino acid groups on the helical conformation of the main chain and the enantioseparation were investigated. In DMF, CD intensities of PPA-1b and PPA-2b having R-configuration on the second chiral center were higher than those of PPA-1a and PPA-2a having S-configuration at the same position, indicating that PPA-1b and PPA-2b may possess more stereoregular helix senses. The chiral recognition abilities of these polymers obviously depended on the main chain helical conformation induced by different coating solvents and the chiral centers in the pendant. Some racemates were better resolved on PPA-1b and PPA-2b, especially the racemic 1-phenylprop-2-yn-1-ol (8) which could be better resolved on PPA-2b than on the well-known commercial chiral column AD-H.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...