An l-cysteine-mediated iodide-catalyzed reaction for the detection of I−†
Abstract
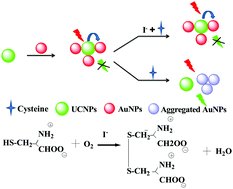
In this study, a highly selective and eco-friendly fluorescent sensor consisting of upconversion (UCNPs) and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) was developed for the detection of iodide (I−). The negatively charged AuNPs were able to electrostatically adsorb on the positively charged UCNPs, leading to the fluorescence quenching of the UCNPs. In the presence of L-cysteine, AuNPs were released from the surface of the UCNPs and aggregated due to the Au–S interactions that occurred between the AuNPs and L-cysteine, which resulted in the fluorescence recovery of the UCNPs. Upon the addition of I−, the fluorescence of the UCNPs was gradually quenched meaning that I− catalyzes the oxidation of L-cysteine, preventing the aggregation of AuNPs and forming a fluorescence resonance energy transfer system. The I−-catalyzed oxidation reaction provides a method for the L-cysteine-triggered sensor to detect I−, using L-cysteine to modulate the fluorescence signal in an eco-friendly manner. Based on the above special detection strategies, this sensor has excellent selectivity for I− even in a complex matrix such as urine, which is much better than most assays for I−. Under the optimal conditions, the sensor allows the quantitative analysis of I− with a detection limit of 55 nM. The high selectivity, sensitivity and environmental friendliness of the sensor proves that it has the potential for the detection of I− in actual samples. Most importantly, the excellent results of the sensor for the detection of I− in urine prove that the probe can be used as an ideal tool in clinic diagnoses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...