Green synthesis of methyl gallate conjugated silver nanoparticles: a colorimetric probe for gentamicin†
Abstract
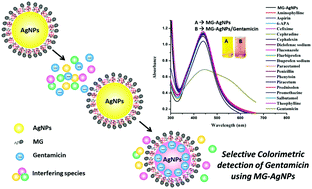
Gentamicin is a broad spectrum antibiotic employed for the cure of infections caused by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. It is eliminated through urine in the unmetabolized and microbiologically active form, leading to the emergence of gentamicin-resistant bacteriocoenosis. Green synthesis of methyl gallate conjugated silver nanoparticles (MG–AgNPs) is reported in this study. The synthesized MG–AgNPs were found to be stable at high temperature, in the pH range 4 to 8, and with up to 100 mM NaCl concentration in the solution. Further, the synthesized MG–AgNPs were employed as a selective and sensitive probe for the detection of gentamicin. The proposed colorimetric aggregation sensor significantly detected gentamicin over a wide range of concentrations in the presence of other interfering drugs and metal ions. UV-visible spectroscopy, FTIR, and atomic force microscopy were employed to confirm the sensing phenomenon. The binding ratio of MG–AgNPs with gentamicin was found to be equimolar. The limit of detection and quantification were found to be 0.29 μM and 1 μM, respectively, in the concentration range of 1–100 μM. The proposed sensor significantly detects gentamicin in environmental waters, human blood plasma, serum, and urine.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...