Synthesis of dendrimer functionalized adsorbents for rapid removal of glyphosate from aqueous solution
Abstract
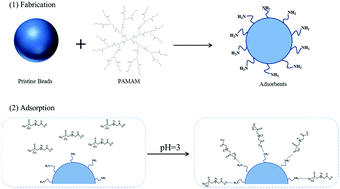
Recently, the growing abuse of glyphosate herbicides in agricultural production has caused widespread accumulation of glyphosate in the environment, which is threatening the health or life of human beings and animals. To solve this problem, novel dendrimer grafted adsorbents were proposed for the rapid and efficient removal of glyphosate from water samples. These adsorbents were synthesized by grafting poly(amidoamine) dendrimers (PAMAM) onto poly(styrene-divinyl benzene-glycidylmethacrylate) beads. The morphological structure and chemical composition of the adsorbents were investigated by SEM, the BET method, FTIR spectroscopy, XPS and elemental analysis. Batch adsorption experiments were performed in glyphosate standard solutions with different pH, temperatures, and initial concentrations. Under the optimized conditions, adsorption equilibrium was attained rapidly within 5 min. Experimental data were correlated well with the pseudo-second-order model and the Langmuir model. The effect of temperature was also discussed by the thermodynamic parameters. Unlike other glyphosate adsorbents, their adsorption capabilities could be easily controlled by varying the generation of PAMAM dendrimer used. In addition, regeneration experiments showed that the adsorbents exhibited good reproducibility. When applied in the purification of contaminated drinking water, the removal efficiency of the adsorbents could be more than 95%.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...