The Knoevenagel condensation using quinine as an organocatalyst under solvent-free conditions†
Abstract
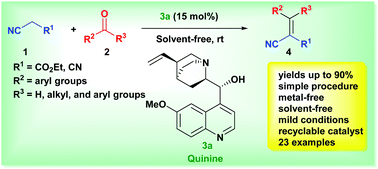
The Knoevenagel condensation between active methylene compounds and aromatic carobonyl compounds has been developed using quinine as an organocatalyst to afford various electrophilic alkenes in excellent yields (up to 90%). In the presence of a catalytic amount of quinine (15 mol%), the reaction proceeded at room temperature (RT) under solvent-free conditions. In this green approach, the organocatalyst was recovered and recycled for up to four cycles without appreciable loss of activity.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...