Multifunctional luminescent coordination polymers based on tricarboxylic acid for the detection of 2,4-dinitrophenol and iron(iii) and aluminum(iii) ions†
Abstract
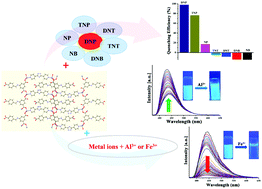
A multifunctional luminescent Zn(II)-coordination polymer, namely {[Zn2(μ3-HCIP)2(μ-bpt)]·2H2O}n (1) (H3CIP= 5-(4-carboxybenzylamino)isophthalic acid, bpt = 3,5-bis(pyridin-4-yl)-1,2,4-triazole), was prepared by using tricarboxylic acid (H3CIP) and bpt ligands under solvothermal conditions and characterized by elemental analysis, IR spectroscopy, thermogravimetric analysis, and powder and single-crystal X-ray diffraction. Single crystal X-ray results showed that the HCIP ligand which was partly deprotonated acted as a tridentate bridging ligand and displayed a new coordination mode. Complex 1 exhibited 2D layers which were further extended to 3D supramolecular structures with hydrogen bonding. 1 showed blue emission in the solid state and fluorescence titration studies indicated that the DMF suspension of 1 exhibited highly selective and sensitive detection towards 2,4-dinitrophenol (DNP) in the presence of other nitroaromatic compounds and the detection limit of 1 for sensing DNP was 0.173 ppm. 1 was able to selectively detect Fe3+ ions over the other competing metal ions with the detection limit of 3.3 ppm. In addition, 1 dispersed in methanol sensitively and selectively detected Al3+ ions via luminescent enhancement over the other interfering metal ions with the detection limit of 0.764 ppm. The results demonstrated that 1 could be usable as a luminescent sensor for the detection of DNP and Fe3+ and Al3+ ions.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...