Design and gelation behaviors of cholesterol-based derivatives as organogelators: an investigation of the correlation between molecular structures and gelation behaviors†
Abstract
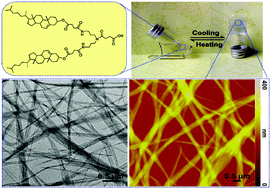
This paper describes the investigation of the correlation between molecular structures and gelation behaviors. First, three types of cholesterol-based compounds as potential gelators were synthesized and their gelation behaviors in various organic solvents were investigated. We found that only molecules with two cholesteryl moieties and a carboxylic group could form organogels in cyclohexane, toluene, o-xylene, m-xylene and p-xylene. The organogels were thoroughly investigated using the vial inversion method, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), atomic force microscopy (AFM), Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction (XRD). The gel-to-sol transition temperature indicated that the organogels exhibited outstanding thermal stabilities. The TEM and AFM measurements showed that the supramolecular structures of the organogels were composed of fibrous aggregates. On the basis of FT-IR characterization and XRD analysis, a probable molecular packing model of gelators in aggregates has been proposed. The present investigation suggested that the carboxylic group and the number of cholesteryl moieties have an important influence on the gelation behavior. Also, it possibly provided some insights into the design of new types of gelators.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...